Diabetes Management
The Impact of Intermittent Fasting on Blood Sugar Control
2 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 21 November 2023
Share this article
0
0 like

Intermittent fasting has gained significant attention in recent years, not only as a weight loss strategy but also for its potential health benefits. One area of interest is its impact on blood sugar control, especially for individuals managing diabetes or at risk of developing the condition.
Understanding Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. Common methods include the 16/8 method (16 hours of fasting and an 8-hour eating window), the 5:2 method (eating normally for five days and significantly reducing calorie intake for two non-consecutive days), and the eat-stop-eat method (24-hour fasting once or twice a week).
Blood Sugar Levels and Insulin Sensitivity
Studies have suggested that intermittent fasting may play a role in improving insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels. During fasting periods, the body's insulin levels decrease, leading to a more efficient use of insulin when it is released. This enhanced insulin sensitivity can help regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of insulin resistance, a common precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Effects on Weight Loss
One of the primary ways intermittent fasting may benefit blood sugar control is through weight loss. Excess body weight is a risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes, and intermittent fasting has been shown to contribute to weight loss by promoting calorie restriction and fat burning.
Inflammatory Response and Cellular Health
Intermittent fasting has been associated with a reduction in inflammation and improvements in cellular health. Chronic inflammation is linked to insulin resistance and impaired blood sugar control. By reducing inflammation, intermittent fasting may positively influence insulin sensitivity.
While promising, it's crucial to approach intermittent fasting with caution, especially for individuals with diabetes or other health conditions. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to one's diet or fasting routine. The impact of intermittent fasting can vary among individuals, and what works for one person may not be suitable for another.
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting shows promise as a tool for blood sugar control, potentially benefiting those at risk of or managing diabetes. However, individual factors, medical history, and preferences must be considered. As with any lifestyle change, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate approach for achieving optimal blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
Diabetes Management
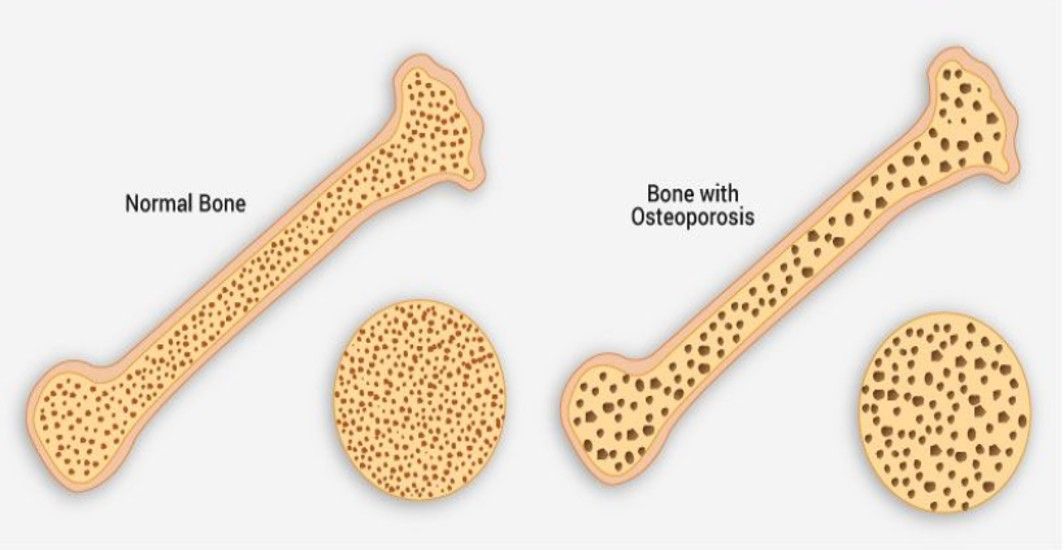
Bone Health for Diabetics: Minimizing Osteoporosis Risk
The impact of diabetes on bone health is often overlooked. However, it's crucial to understand that diabetes increases the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Adopting a balanced diet, staying active, effectively managing blood glucose levels, and routine health checks can help maintain bone health.

Diabetes Management
Understanding Sleep Hygiene and Optimal Sleep Patterns
Embracing good sleep hygiene helps in establishing a regular sleep-wake cycle, leading to improved physical and mental health. This includes a consistent sleep schedule, bedtime routines, and avoiding habits like irregular sleep timings and excessive caffeine intake that hinder sound sleep.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
Best Tips for Managing Diabetes with Food Allergies
Managing diabetes with food allergies is a balancing act that requires careful dietary planning and regular consultations with your doctors. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods, identifying and avoiding allergens, addressing micronutrient deficiencies, and staying hydrated are key strategies. An integrated approach, coupled with support from programmes like Apollo Super 6, can help you manage this challenge successfully.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Bone Health for Diabetics: Minimizing Osteoporosis Risk
The impact of diabetes on bone health is often overlooked. However, it's crucial to understand that diabetes increases the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Adopting a balanced diet, staying active, effectively managing blood glucose levels, and routine health checks can help maintain bone health.

Diabetes Management
Understanding Sleep Hygiene and Optimal Sleep Patterns
Embracing good sleep hygiene helps in establishing a regular sleep-wake cycle, leading to improved physical and mental health. This includes a consistent sleep schedule, bedtime routines, and avoiding habits like irregular sleep timings and excessive caffeine intake that hinder sound sleep.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
Best Tips for Managing Diabetes with Food Allergies
Managing diabetes with food allergies is a balancing act that requires careful dietary planning and regular consultations with your doctors. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods, identifying and avoiding allergens, addressing micronutrient deficiencies, and staying hydrated are key strategies. An integrated approach, coupled with support from programmes like Apollo Super 6, can help you manage this challenge successfully.
