Thyroid Exercise
Discover how regular exercise can help manage thyroid health, improve metabolism, balance hormones, and enhance overall well-being.

Written by Dr Sonia Bhatt
Last updated on 3rd Jul, 2025
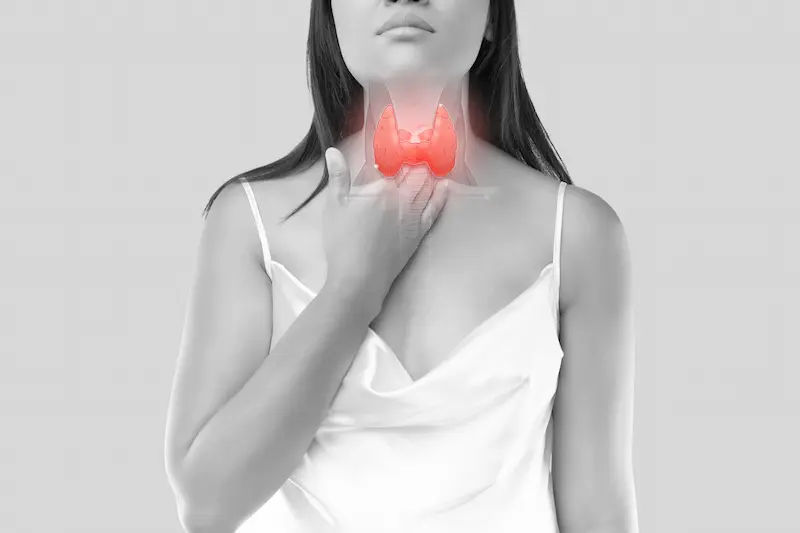
The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland responsible for producing hormones that regulate the metabolism, development and growth of the human body. Located at the base of the neck, this gland is made of two lobes and connected by a thin tissue called the isthmus. The thyroid gland produces two essential hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which influence nearly every cell and tissue in the body. Therefore, despite its small size, this organ is intricately linked with the entire physiological process of human beings.
Now, the thyroid hormones play a fundamental role in maintaining the body's energy balance, metabolic rate, and overall functionality. Alongside the metabolism and absorption of energy, the thyroid gland also influences bone health, heart health, muscle strength, etc. Hence, keeping this vital organ safe, functional, and healthy is of utmost importance to every human being. In this process, regular exercise plays a pivotal role.
Consult Top Doctors For Thyroid Symptoms
The Role of Exercise in Thyroid Health
Regular exercise is pivotal for thyroid health. Here is how it helps:
- Regular exercise improves metabolic functions through the increased production of T3 and T4 hormones. So, it keeps the thyroid active and working.
- It also reduces stress and cortisol levels, which creates an optimal level for the thyroid gland to function smoothly.
- Regular exercise also improves hormone conversion. With everyday exercise, the circulation of the hormones improves, which supports better hormonal conversion and distribution throughout the body.
- Since regular workout sessions control the inflammation levels in the body, they support thyroid health and reduce the chances of developing Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Benefits of regular physical activity for thyroid health
Engaging in regular exercise provides a host of benefits for individuals managing thyroid conditions. Some of the highlights are:
- Better weight management
- Improved energy levels
- Better cognitive functions
- Enhanced cardiovascular health
- Better bone health
Types of Exercises Beneficial for Thyroid Health
Physical activity plays an important role in managing thyroid levels, and different types of exercises have a variety of benefits.
- Aerobic exercises : This form of exercise is good for improving cardiovascular health and metabolism. These help increase the heart rate to encourage circulation. Some examples are walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming.
- Strength training: Engaging in strength training activities like lifting weights and using resistance bands helps individuals with thyroid. It helps with muscle weakness and reduces bone density.
- Yoga and flexibility exercises: Certain yoga poses, such as the shoulder stand and fish pose, as well as practices like stretching or Pilates, stimulate the thyroid gland.
Exercise Recommendations for Different Thyroid Conditions
Depending on whether an individual has hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, different types and intensities of exercise are recommended.
Hypothyroidism and physical activity
- Moderately intense exercises are highly beneficial for individuals with hypothyroidism as they help boost energy levels and manage common symptoms like weight gain and fatigue. Here are some suggestions:
- Aerobic Exercises: Exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling are excellent low-impact options for increasing circulation and managing weight gain, both of which are common concerns for those with hypothyroidism. These exercises help improve heart health, enhance stamina, and elevate mood by releasing endorphins. Aim for 20 to 30 minutes of aerobic activity four to five times a week, adjusting the intensity to match your fitness level.
- Strength Training: Hypothyroidism often leads to muscle weakness and a slower metabolism, making strength training a key component of any exercise routine. These include exercises like resistance band workouts, light weightlifting, or bodyweight exercises (e.g., squats, lunges, and push-ups)
- Flexibility and Relaxation: Yoga, Pilates, and gentle stretching help in relieving stiffness, which is a common complaint among people with hypothyroidism. These activities also promote relaxation and help lower stress levels. For example, child’s pose, cat-cow stretch, or gentle backbends.
Hyperthyroidism and exercise
For hyperthyroidism, exercise routines should aim to lower stress levels, maintain muscle mass, and support cardiovascular health without overburdening the body.
- Yoga and Relaxation Techniques: Hyperthyroidism often heightens stress and anxiety. Poses like a child’s pose, forward fold, and legs up-the-wall promote mental relaxation and regulate the nervous system.
- Strength Training with Light Weights: Use light weights or resistance bands to perform controlled movements such as bicep curls, squats, or wall push-ups.
- Low-Impact Aerobics: Low-impact cardiovascular activities like walking, cycling, or swimming in your routine help improve heart rate. These exercises help strengthen the heart without placing excessive strain on it.
Precautions While Exercising with Thyroid Conditions
Exercise can be very helpful in controlling thyroid health, but it must be used with caution. Here are some important safety measures to think about:
- Keeping an eye on energy levels and fatigue: Fatigue and poor energy levels are common symptoms of thyroid disorders, particularly hypothyroidism. Therefore, a workout routine in such conditions should be of low intensity at first, then gradually increased to suit the health condition of the individual.
- Monitoring heart rate and stress levels: Exercises that raise your heart rate significantly should be avoided since thyroid disorders like hyperthyroidism might result in an elevated heart rate. Use a heart rate monitor to stay within the safe range and concentrate on low-impact exercises like yoga, strolling, or swimming.
- Developing a Safe Exercise Plan: To ensure safety and maximise benefits, it is essential to design a workout regimen that is specific to your thyroid levels and demands. Here's how to tackle it with consideration:
- Consulting with healthcare professionals: It's crucial to speak with your endocrinologist or doctor before beginning any workout. They can assist you in comprehending how your thyroid may impact your heart health, energy levels, and ability to engage in physical exercise.
- Setting realistic fitness goals: Setting attainable goals and practising self-compassion is crucial while managing a thyroid condition. Set modest, doable goals at first, such as stretching lightly or going for a daily 15-minute stroll.
Impact of Exercise on Thyroid Medication
Thyroid medicine and exercise complement one another, but they can also have important interactions. Here are more details:
- Interaction between exercise and medication absorption: Levothyroxine and other thyroid medications require the proper environment to function, which is typically an empty stomach with no distractions. So, individuals need to follow the doctor's recommendations regarding when to take the medicine and when to work out to prevent hiccups.
- Adjustments needed in medication with increased physical activity: Every human body reacts differently to thyroid medication under intense workout sessions. Therefore, the medication needs to be adjusted as regular movement can increase metabolism and potentially alleviate some thyroid symptoms.
Diet and Nutrition along with Exercise
Exercise is only one aspect of thyroid health; diet is just as important. Exercise and a healthy, nutrient-dense diet can complement each other to promote your thyroid and general health.
- Importance of a balanced diet: A healthy diet provides the human body with the energy it needs to be active and maintain optimal thyroid function. Individuals can make sure they are getting the required nutrients by eating a range of entire foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Nutrients that support thyroid function: Here are a few nutrients crucial to add to the diet:
- Fish and iodised salt contain iodine, which aids in the synthesis of hormones.
- Zinc (found in meat and chickpeas) controls hormones, while selenium (found in Brazil nuts and eggs) protects the thyroid.
- Iron (found in lean meats and spinach) supports healthy thyroid hormone activity
- Vitamin D promotes hormonal balance
Monitoring Progress and Making Adjustments
When managing thyroid health, keeping track of the progress is very important as it helps individuals understand what’s working and what needs tweaking. Here are some suggestions:
- Tracking physical and thyroid health outcomes: Over time, individuals need to pay attention to how their body feels. An increase in the energy levels, elevation of the mood and improvement of other symptoms suggest that the new regime is working.
- Adjusting exercise routines based on progress: Based on the initial results, individuals need to alter their exercise routines. As they build endurance and stamina, they can increase the time and intensity of the regime. It will slowly deliver results and improve thyroid health.
Conclusion
Lifestyle adjustments are necessary to maintain thyroid function, and exercise is a major contributor to it. Exercise can help individuals manage symptoms like weight fluctuations or exhaustion and increase energy levels and hormone levels.
Having said that, the impact of thyroid disorders is not the same for everyone. So, opting for a more customised exercise plan is important to address specific issues. It helps the individuals notice better and faster results and get better easily.
Consult Top Endocrinologist
Consult Top Doctors For Thyroid Symptoms
Dr Sumanth R
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Chaithanya R
Internal Medicine Specialist Diabetologist
16 Years • MBBS, MD Internal Medicine, Fellowship in Diabetes(UK), CCEBDM(PHFI)
Bangalore
Apollo Clinic Bellandur, Bangalore
(75+ Patients)

Dr. Anand Ravi
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Shruthi B
Endocrinologist
20 Years • MBBS,MD ( GEN MED) DM (ENDOCRIONOLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Shrikrishna V Acharya
Endocrinologist
25 Years • MBBS, MD, DM(Endocrinology), MRCP (Endocrinology)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
Consult Top Endocrinologist
Dr Sumanth R
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Chaithanya R
Internal Medicine Specialist Diabetologist
16 Years • MBBS, MD Internal Medicine, Fellowship in Diabetes(UK), CCEBDM(PHFI)
Bangalore
Apollo Clinic Bellandur, Bangalore
(75+ Patients)

Dr. Anand Ravi
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Shruthi B
Endocrinologist
20 Years • MBBS,MD ( GEN MED) DM (ENDOCRIONOLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Shrikrishna V Acharya
Endocrinologist
25 Years • MBBS, MD, DM(Endocrinology), MRCP (Endocrinology)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru