Primary Hypothyroidism: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover everything about primary hypothyroidism, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Learn how this thyroid condition affects overall health and how to manage it effectively.

Written by Dr Sonia Bhatt
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
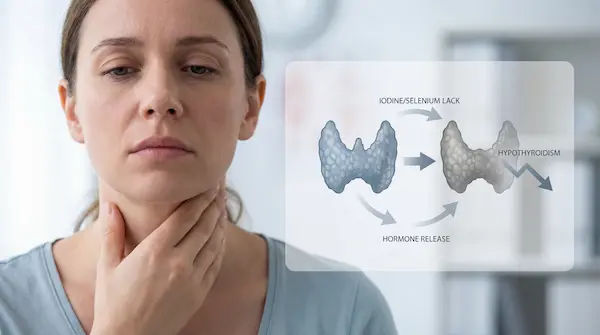
Primary hypothyroidism is a condition that directly affects one’s thyroid gland and causes low hormone production. It is the most common type of hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) that is mainly caused by autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s disease.
Primary hypothyroidism can cause multiple metabolic disorders and severe complications if not treated on time. Keep reading to learn more about the symptoms, causes, and treatment methods of this condition.
Symptoms and Signs of Primary Hypothyroidism
Primary hypothyroidism has varied symptoms that usually differ from one person to another. Here are some of the symptoms that are common in most patients:
- Gaining weight
- Dryness in skin
- Pain in muscle
- Constipation
- Fatigue
- Concentration difficulties
- Cold sensitivity, etc.
In some cases, the metabolic effect of primary hypothyroidism affects an individual’s mental health, causing depression. The cognitive function of the brain is supported by proper metabolic processes. As this process is disrupted by primary hypothyroidism, mental health is affected.
Consult Top Doctors For Thyroid Symptoms
Causes of Primary Hypothyroidism
Hashimoto’s disease is an autoimmune condition that causes an individual's immune system to attack their thyroid gland. In most cases, primary hypothyroidism is caused by Hashimoto’s disease.
However, this is not the only reason. Other causes of primary hypothyroidism include the following:
- Viral thyroiditis
- Deficiency of dietary iodine
- Congenital disease
- Some specific drugs, etc.
Individuals undergoing hyperthyroidism treatment may also get primary hypothyroidism. This is because the radioactive iodine therapy used to treat hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) destroys thyroid hormones, causing hypothyroidism.
In diseases like thyroid cancer, the thyroid gland is removed through surgery, which stops the thyroid hormone production, causing hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism may also develop in women while giving birth and in people above 60 years.
Risk Factors Associated with Primary Hypothyroidism
Primary hypothyroidism is a type of hypothyroidism. Thus, risk factors related to hypothyroidism can also affect an individual with primary hypothyroidism conditions. Here are some of them:
- Genetic factors
- Pregnancy
- Autoimmune disease
- Intaking or discontinuing certain medications
- Radiation therapy of the head and neck
- Thyroid surgery, etc.
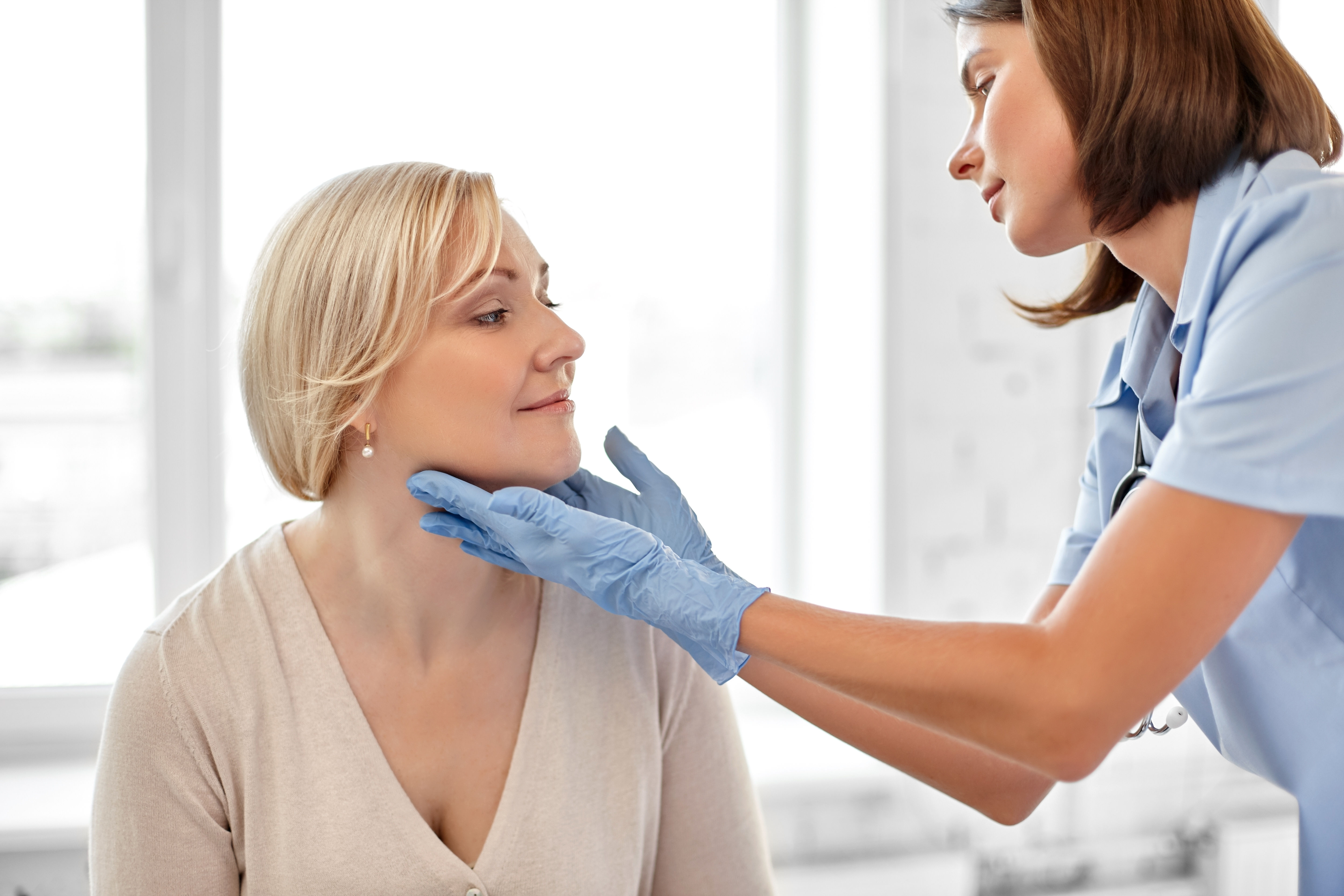
Diagnosis of Primary Hypothyroidism
The first step in diagnosing primary hypothyroidism is clinical assessment, such as analysing the signs and symptoms. Doctors suggest blood tests after noticing the symptoms to determine the thyroid hormone levels in an individual’s body.
Low levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroxine (T4), and triiodothyronine (T3) in individuals’ bodies determine they have primary hypothyroidism.
Check Your Thyroid Levels
Treatment Methods of Primary Hypothyroidism
As primary hypothyroidism is associated with inadequate hormone production, its treatment involves medicines that can replace the thyroid hormones in a person's body. Initially, doctors prescribe a low dose and modify the dosage as per the individual's requirements.
Synthetic thyroid hormones are provided in the form of medicines to treat primary hypothyroidism. Medicines containing levothyroxine are used as a replacement for T4 and liothyronine is used as a replacement for T4 hormones. Patients need to take these medicines regularly as per the doctor’s prescription until the normal thyroid range is reached.
Once the patients stop these medicines, the symptoms of primary hypothyroidism will come back. Thus, individuals need to undergo medication for a lifetime to keep primary hypothyroidism under control.
Note: Drugs for calcium or iron supplements and certain other medications can interfere with the treatment process for primary hypothyroidism. They should not be taken within 4 hours of levothyroxine as they can reduce absorption. So, patients need to inform their doctor beforehand about such situations.
Complications of Primary Hypothyroidism
Primary hypothyroidism can cause several serious complications if left untreated. These include:
Cardiovascular issues such as heart disease due to elevated cholesterol levels and increased risk of atherosclerosis.
- Mental health problems like depression and cognitive decline may also occur.
- In women, untreated hypothyroidism can result in menstrual irregularities and complications during pregnancy, such as birth defects, miscarriage, etc.
- In extreme cases, myxedema coma—a rare but life-threatening condition—can develop due to severe prolonged hypothyroidism.
Prognosis for Primary Hypothyroidism
Primary hypothyroidism is not completely curable. However, it can be controlled by timely diagnosis and proper medication. Lifelong medication to replace the thyroid hormone in one’s body can keep primary hypothyroidism under control.
Preventative Measures of Primary Hypothyroidism
Changes in food habits and lifestyle may help prevent medical conditions like primary hypothyroidism. Here are some of them:
- Including foods rich in selenium and magnesium can regulate thyroid hormone levels in an individual’s body. Consuming nuts and seeds can supply these nutrients in one’s body and help in thyroid control.
- Regular exercises like strength training, and cardiovascular training, can help one’s muscles and heart function properly. It lowers the risks of primary hypothyroidism.
Conclusion
Primary hypothyroidism is a manageable but potentially serious condition that requires awareness and right management. Understanding its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and complications is essential for effective care.
With appropriate hormone replacement therapy and regular monitoring, individuals diagnosed with primary hypothyroidism can minimise risks associated with the disorder.
Consult Top Endocrinologist
Consult Top Doctors For Thyroid Symptoms

Dr. Ramya Varada
Endocrinologist
10 Years • MD, DM
Chinagadila
Apollo Hospitals Health City Unit, Chinagadila
(150+ Patients)

Dr. Gunjan Garg
Endocrinologist
15 Years • MBBS, MD(Medicine), DM( Endocrinology)
Noida
Apollo Hospitals Sector 26, Noida
(75+ Patients)

Dr. Nupur Tandon
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
16 Years • MBBS, PG DIPLOMA IN Diabetes Management, Specialist in diabetes and thyroid disorders (CCEBDM)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, Sarjapur Road, Bengaluru
(25+ Patients)
Dr Sumanth R
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Mary Susan K S
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MD INTERNAL MEDICINE
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, Sarjapur Road, Bengaluru
(25+ Patients)
Consult Top Endocrinologist

Dr. Ramya Varada
Endocrinologist
10 Years • MD, DM
Chinagadila
Apollo Hospitals Health City Unit, Chinagadila
(150+ Patients)

Dr. Gunjan Garg
Endocrinologist
15 Years • MBBS, MD(Medicine), DM( Endocrinology)
Noida
Apollo Hospitals Sector 26, Noida
(75+ Patients)

Dr. Nupur Tandon
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
16 Years • MBBS, PG DIPLOMA IN Diabetes Management, Specialist in diabetes and thyroid disorders (CCEBDM)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, Sarjapur Road, Bengaluru
(25+ Patients)
Dr Sumanth R
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Mary Susan K S
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MD INTERNAL MEDICINE
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, Sarjapur Road, Bengaluru
(25+ Patients)