Heart Conditions
Why You Should Regularly Check Your Blood Pressure at Home
5 min read
By Apollo 24/7, Published on - 10 June 2021, Updated on - 21 February 2025
Share this article
6
13 likes
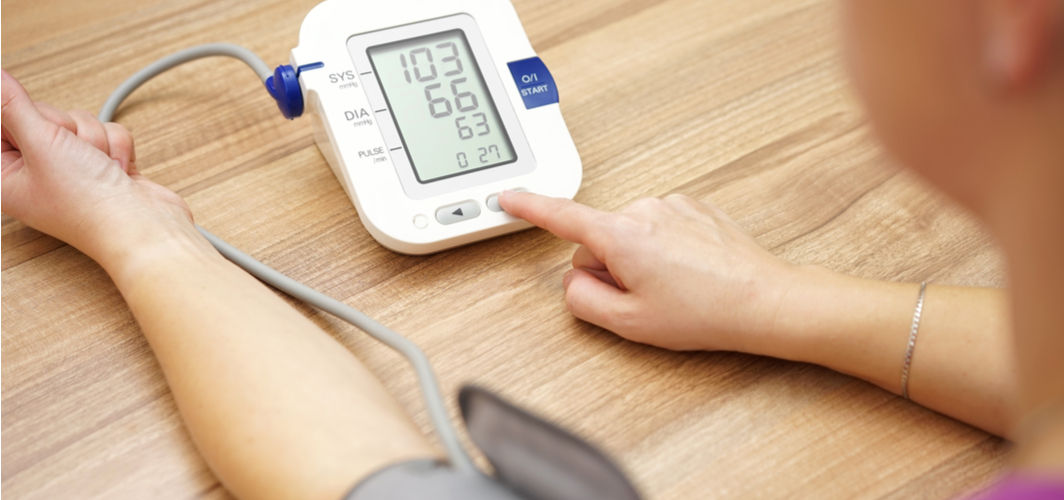
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 1.3 billion people in the world suffer from high blood pressure, also called hypertension. Left untreated, hypertension can become a serious condition and result in severe health consequences such as angina, arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat), heart attack, heart failure, stroke and even death. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor blood pressure frequently to prevent such events.
Blood pressure can be measured either in a medical setup (with the help of a device known as a sphygmomanometer) or at home using a digital blood pressure monitor.
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the amount of pressure exerted by the blood on the vessel wall while travelling through the body. Blood pressure (BP) is measured in two forms:
- Systolic blood pressure: It is the pressure exerted by the heart when pushing the blood out to the artery wall. It is the upper limit of the blood pressure value and is recorded when the heart beats.
- Diastolic blood pressure: It is the pressure exerted by the blood when refilling the heart. It is the lower limit of the blood pressure value and is recorded in the resting period of the heart, between two beats.
Understanding blood pressure values
Blood pressure is considered normal when the readings are 120/80 mm Hg or less, where 120 mm Hg is the systolic BP and 80 mm Hg is the diastolic BP. According to the American Heart Association, the different categories of blood pressure include:
- Low BP: Also known as hypotension, low blood pressure is the state where the BP falls below 90/60 mm Hg. It is a dangerous state and requires immediate medical care.
- Elevated BP: When the systolic BP ranges from 120 to 129 mm Hg and the diastolic pressure is at or below 80 mm Hg, it is called an elevated BP.
- Stage 1 hypertension: In stage 1 hypertension, the systolic BP ranges from 130 to 139 mm Hg and the diastolic pressure ranges from 80 to 89 mm Hg.
- Stage 2 hypertension: In stage 2 hypertension, the systolic pressure ranges from 140 mm Hg or even higher, while the diastolic pressure reaches 90 mm Hg or above.
- Hypertensive crisis: It is a critical stage of hypertension where the systolic blood pressure crosses 180 mm Hg and the diastolic blood pressure exceeds 120 mm Hg. In this stage, immediate medical care is required as the affected person can suffer from multiple organ damage.
Types of blood pressure monitors
Blood pressure can be measured with the help of two types of devices: manual and digital.
1. Manual blood pressure machine
Also called a manual sphygmomanometer, this device is one of the most widely used blood pressure measuring devices in a medical setup. It consists of a cuff that is wrapped around the arm of the patient, a gauge (reading scale), and an inflation bulb. This device is mostly used by medical professionals as it requires a stethoscope to interpret the readings. Manual sphygmomanometers are available in two types:
- Mercury sphygmomanometer: This device is considered the gold standard for measuring blood pressure clinically. In this device, the reading scale contains mercury.
- Aneroid sphygmomanometer: In this device, the reading board does not have mercury but a round gauge for measuring the BP.
2. Digital blood pressure machine
Also called a digital sphygmomanometer, these devices can be used at home without any assistance. The process of using a blood pressure device at home, away from a hospital, is called self-measured blood pressure (SMBP) monitoring. These devices are safe and easy to use and comprise a cuff and a monitor to measure ambulatory blood pressure. Ambulatory monitoring involves measuring the blood pressure at set times (usually every 30 minutes) and requires wearing the cuff for 24 hours.
The accuracy of home blood pressure monitors must be validated once a year by taking it to a medical setup and comparing the values recorded on the devices. Blood pressure can be monitored accurately at home using digital monitors unless one suffers from heart rhythm conditions like atrial fibrillation, arrhythmia, etc.
Why should one have a blood pressure monitor at home?
The benefits of having a blood pressure machine at home include:
- Home BP monitor machines can help measure blood pressure daily, which can prevent sudden health complications such as heart failure and stroke.
- Digital BP machines can monitor ambulatory blood pressure 24 hours a day, which can help in diagnosing masked hypertension, thereby reducing the risk of organ damage.
- Since digital blood pressure machines are small in size, they can be carried around while travelling somewhere.
- Digital BP machines can be extremely helpful to those who cannot visit a doctor regularly to get their blood pressure measured such as old and bed-ridden people and pregnant women.
- Medical centres often trigger anxiety and spike the blood pressure of many people, which is known as white coat hypertension. Digital BP machines can help measure the correct blood pressure of such patients.
Things to keep in mind when measuring blood pressure at home
- Do not consume caffeine or smoke 30 minutes before measuring BP.
- Avoid exercising or even walking 30 minutes before BP measurement.
- Empty the bladder before taking a measurement.
- Do not take the measurements from over the clothing. Place the cuff on the bare arm.
- Do not talk while measuring the blood pressure.
- If blood pressure has to be measured again, wait for 5 minutes before measuring.
When to contact a doctor?
One should consult a doctor if they experience:
- Very high or very low blood pressure:
- 180/120 mm Hg or higher
- 90/60 mm Hg or lower
- Severe headache
- Blurred vision
- Profuse sweating
- Difficulty sleeping
- Facial flushing
- Anxiety
- Dizziness
Conclusion
Both high and low blood pressure can be extremely dangerous and can result in serious health consequences. Blood pressure monitors such as digital sphygmomanometers can be extremely helpful in measuring BP regularly at home without professional help. A person diagnosed with hypertension or hypotension can measure their BP using such devices and record them in a journal. These readings would help the doctor decide the dose and class of medications one may require.
If you have any questions related to heart health, you can:
Heart Conditions
Leave Comment
Recommended for you

Heart Conditions
Signs Of Heart Problems To Look Out For During Winters
Not all signs of heart problems are as evident as chest pain, and there are other subtle symptoms that can be early warning signs.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Heart Conditions
Hypertension Causes and Risks: Your Guide to Prevention
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is when the blood exerts excessive force against the artery walls, posing serious health risks. Due to high blood pressure, there is increased pressure on the heart and other organs while functioning, potentially leading to heart attacks, strokes, and kidney failure. Additionally, it can damage blood vessels, eyes, and the brain. Today, we will explore everything related to hypertension: what it is, its symptoms, causes and risk factors, and prevention strategies.

Heart Conditions
The Truth about Coffee and Heart Health
While some research suggests that coffee helps in maintaining heart health, others indicate that excess coffee consumption can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories
Lower Your Cholesterol Naturally with These 7 Foods
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Heart Conditions
Signs Of Heart Problems To Look Out For During Winters
Not all signs of heart problems are as evident as chest pain, and there are other subtle symptoms that can be early warning signs.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Heart Conditions
Hypertension Causes and Risks: Your Guide to Prevention
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is when the blood exerts excessive force against the artery walls, posing serious health risks. Due to high blood pressure, there is increased pressure on the heart and other organs while functioning, potentially leading to heart attacks, strokes, and kidney failure. Additionally, it can damage blood vessels, eyes, and the brain. Today, we will explore everything related to hypertension: what it is, its symptoms, causes and risk factors, and prevention strategies.

Heart Conditions
The Truth about Coffee and Heart Health
While some research suggests that coffee helps in maintaining heart health, others indicate that excess coffee consumption can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.