Diabetes Management
Is There a Connection Between Diabetes, Polydipsia, and Polyuria?
2 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 22 December 2023, Updated on - 22 February 2024
Share this article
0
0 like

Diabetes mellitus often manifests with symptoms such as polydipsia (excessive thirst) and polyuria (increased urine production). Let’s dive deep into exploring the physiological connections between diabetes and these symptoms.
Hyperglycemia and Osmotic Diuresis:
- In diabetes, either insufficient insulin production (Type 1) or resistance to insulin's action (Type 2) leads to elevated blood glucose levels.
- Hyperglycemia triggers a compensatory mechanism called osmotic diuresis.
- Excess glucose in the bloodstream is filtered into the urine, drawing water from cells and tissues into the urine.
Polyuria - Increased Urine Production:
- Osmotic diuresis results in an increased volume of urine production.
- The kidneys work to eliminate the excess glucose by excreting it in the urine.
- This heightened urine output is a key contributor to polyuria.
Dehydration and Thirst Response:
- As the body loses significant amounts of fluid through increased urine production, dehydration sets in.
- Dehydration triggers a response from the brain, signaling an increased sensation of thirst.
- Polydipsia, or excessive thirst, is the body's attempt to restore the water balance disrupted by osmotic diuresis.
Cellular Dehydration and Thirst Mechanism:
- Hyperglycemia leads to cellular dehydration as water is drawn out of cells.
- Cellular dehydration activates the thirst mechanism in the brain.
- Polydipsia serves as a physiological response aimed at replenishing lost fluids and mitigating cellular dehydration.
Feedback Loop and Persistent Symptoms:
- The cycle of hyperglycemia, osmotic diuresis, dehydration, and increased thirst creates a feedback loop.
- Despite consuming large quantities of water to alleviate thirst, individuals with diabetes may find the symptoms persist due to the underlying glucose imbalance.
Impact on Overall Health:
- Uncontrolled polydipsia and polyuria can lead to electrolyte imbalances and dehydration, affecting overall health.
- Persistent dehydration can contribute to complications such as kidney dysfunction and cardiovascular issues.
Managing Polydipsia and Polyuria:
- Effective diabetes management involves addressing the root cause - elevated blood glucose levels.
- Lifestyle modifications, including adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity, are essential.
- Medication or insulin therapy may be necessary to regulate blood glucose levels effectively.
Regular Monitoring and Intervention:
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial to detect and address fluctuations promptly.
- Healthcare professionals play a vital role in providing guidance, adjusting treatment plans, and ensuring optimal diabetes management.
Conclusion
The connection between diabetes, polydipsia, and polyuria is due to hyperglycemia, osmotic diuresis, and the body's compensatory mechanisms. Understanding these physiological processes is essential for individuals with diabetes and healthcare providers to effectively manage symptoms and prevent complications associated with uncontrolled glucose levels.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
Managing Diabetes in Pets: An Overview and Signs to Look Out For
Our furry friends can also fall prey to diabetes. With symptoms including increased thirst and urination, weight loss despite a normal or increased appetite, it's crucial to stay vigilant. Early detection followed by proper management like regular vet check-ups, insulin therapy, and dietary changes can help your pets lead a healthy life.
Diabetes Management
Fighting Diabetes and Fatty Liver Disease through a Healthy Lifestyle
Understanding the connection between diabetes and fatty liver disease can lead to better prevention and management strategies. By maintaining a healthy weight, eating balanced meals, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol intake and going for regular screenings, you can keep both conditions in check.

Diabetes Management
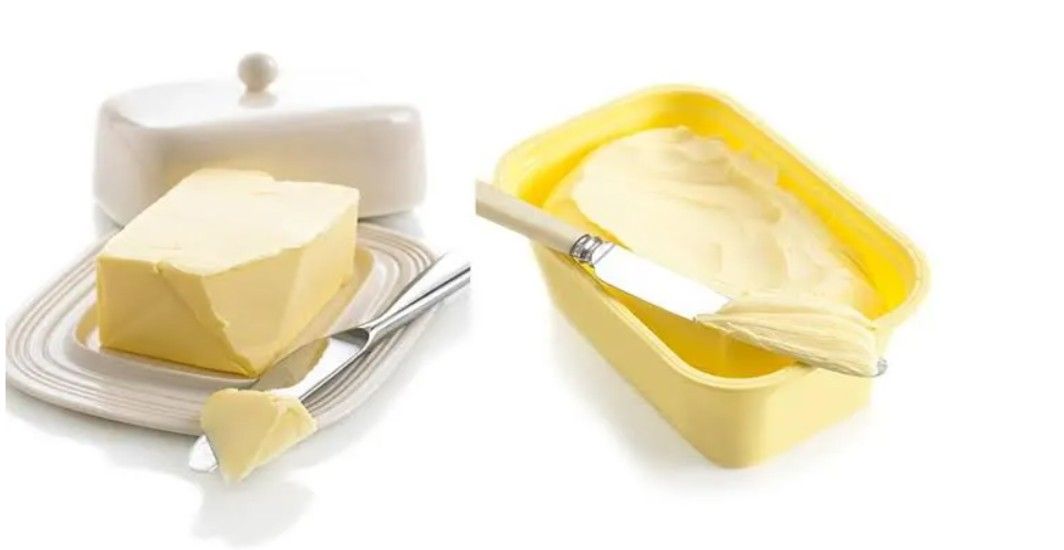
Butter or Margarine: A Guide for Diabetics
Are you debating between butter and margarine if you're a diabetic? Both can be included in your diet—the key lies in moderation and selecting healthier alternatives. Prioritising monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats helps maintain heart health.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
Managing Diabetes in Pets: An Overview and Signs to Look Out For
Our furry friends can also fall prey to diabetes. With symptoms including increased thirst and urination, weight loss despite a normal or increased appetite, it's crucial to stay vigilant. Early detection followed by proper management like regular vet check-ups, insulin therapy, and dietary changes can help your pets lead a healthy life.

Diabetes Management
Fighting Diabetes and Fatty Liver Disease through a Healthy Lifestyle
Understanding the connection between diabetes and fatty liver disease can lead to better prevention and management strategies. By maintaining a healthy weight, eating balanced meals, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol intake and going for regular screenings, you can keep both conditions in check.

Diabetes Management
Butter or Margarine: A Guide for Diabetics
Are you debating between butter and margarine if you're a diabetic? Both can be included in your diet—the key lies in moderation and selecting healthier alternatives. Prioritising monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats helps maintain heart health.

