Diabetes Management
Prevalence of Diabetes in India: These Are The 5 Worst-Affected States
2 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 20 December 2023
Share this article
0
0 like

In a recent Lancet study funded by ICMR and the Health Ministry, the diabetes epidemic in India has taken a more alarming turn than previously estimated by the WHO. The study, published in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, discloses a shocking 101 million people in India grappling with diabetes, constituting a significant 11.4% of the country's population. Furthermore, an additional 136 million individuals are on the precipice of this metabolic disorder, with prediabetes conditions that pose a high risk of developing diabetes in the coming years.
Regional Disparities and Prevalence Rates
Breaking down the data, the study delves into state-wise numbers, revealing notable regional disparities. In terms of diabetes prevalence, southern and northern regions of India exhibit the highest rates. Urban areas consistently show elevated prevalence compared to rural counterparts. The study highlights Goa as the worst-affected state, with a staggering 26.4% prevalence rate. Puducherry follows closely with 26.3%, and Kerala takes the third spot at 25.5%. While Uttar Pradesh, the most populous state, currently has a lower prevalence at 4.8%, the study issues a warning about a potential surge in diabetes cases in the future.
Urban vs. Rural Dynamics
Interestingly, there is no significant difference in prediabetes prevalence between urban and rural areas. This indicates that the risk of diabetes is not confined to urban lifestyles alone, emphasising the need for widespread awareness and preventive measures across all demographics.
Expert Insights and Recommendations
Experts shed light on the contributing factors to the escalating diabetes crisis. Sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy dietary habits, obesity, stress, and genetic predispositions are identified as significant influencers. Urgent interventions are necessary, focusing on regular physical activity, adopting balanced nutrition, managing stress levels, ensuring adequate sleep, and curtailing tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
Urgent Call for Lifestyle Modifications
The Lancet study serves as a wake-up call, urging individuals to prioritise lifestyle modifications. Regular physical activity, including walking, cycling, or structured exercise routines, can aid in maintaining a healthy weight and improving insulin sensitivity. A balanced diet, rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, is crucial. Additionally, limiting sugary beverages and processed foods is emphasised. Managing stress levels, ensuring sufficient sleep, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol intake are deemed essential measures to significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Conclusion
The Lancet study not only unveils startling numbers but also underscores the critical need for immediate action to curb the diabetes epidemic in India. The focus should be on proactive health measures, widespread awareness, and a concerted effort to promote healthier lifestyles across diverse demographics.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
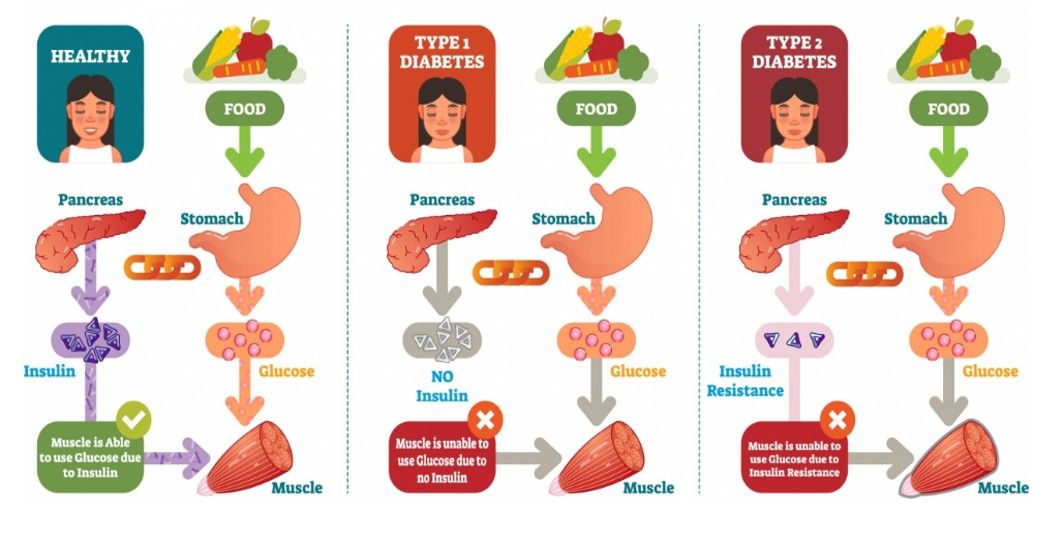
Diabetes Management
Understanding the Different Types of Diabetes
In a world where diabetes is increasingly common, understanding the different types can be crucial for early detection, effective management, and prevention of complications. Whether it's type 1, type 2, gestational, or even rare forms such as monogenic and secondary diabetes, each has its own causes and management strategies. Keep in mind that maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to managing all forms of diabetes.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
Barriers to Diabetes Care In Low-Income Communities
Understanding the barriers to effective diabetes care in low-income communities is crucial for improving health outcomes. Factors like insufficient knowledge, limited healthcare facilities, financial constraints, fragmented services, cultural misconceptions, medication adherence issues, and lack of supportive systems need addressing. Joining comprehensive programmes like Apollo Super 6 can help navigate these challenges and manage diabetes effectively.

Diabetes Management
Are Low-carb Diets Healthy?
A low-carb diet is characterised by the reduced intake of carbohydrates and increased consumption of protein and healthier fats. Most low-carb diets limit carbohydrates to less than 130g per day. Scientific evidence indicates that low-carb diets can positively impact health indicators such as triglycerides, cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, leading to their popularity and adoption for several decades.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Understanding the Different Types of Diabetes
In a world where diabetes is increasingly common, understanding the different types can be crucial for early detection, effective management, and prevention of complications. Whether it's type 1, type 2, gestational, or even rare forms such as monogenic and secondary diabetes, each has its own causes and management strategies. Keep in mind that maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to managing all forms of diabetes.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
Barriers to Diabetes Care In Low-Income Communities
Understanding the barriers to effective diabetes care in low-income communities is crucial for improving health outcomes. Factors like insufficient knowledge, limited healthcare facilities, financial constraints, fragmented services, cultural misconceptions, medication adherence issues, and lack of supportive systems need addressing. Joining comprehensive programmes like Apollo Super 6 can help navigate these challenges and manage diabetes effectively.

Diabetes Management
Are Low-carb Diets Healthy?
A low-carb diet is characterised by the reduced intake of carbohydrates and increased consumption of protein and healthier fats. Most low-carb diets limit carbohydrates to less than 130g per day. Scientific evidence indicates that low-carb diets can positively impact health indicators such as triglycerides, cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, leading to their popularity and adoption for several decades.

