Diabetes Management
The Best Rice Variety for Diabetics: Making Informed Choices
2 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 14 December 2023, Updated on - 07 August 2024
Share this article
0
0 like
_0.jpg?tr=q-80)
Rice is a staple food for millions of people worldwide, known for its versatility and wide range of varieties. However, for individuals with diabetes, choosing the right type of rice can significantly impact blood sugar management. It's essential to make informed choices about the best rice variety to include in a diabetes-friendly diet.

When selecting rice for diabetes management, consider the following factors:
Glycemic Index (GI): The glycemic index measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI are rapidly digested and absorbed, leading to sharp spikes in blood sugar. On the other hand, foods with a low GI cause a slower, more gradual increase in blood sugar levels, promoting better glucose control.
Fiber Content: Fiber is beneficial for diabetes management because it slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. This results in more stable blood sugar levels and a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management, an important aspect of diabetes care.
Nutrient Profile: Rice can vary in its nutrient content, and some types are more nutritious than others. Consider rice varieties that provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which can support overall health and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Here are some rice varieties to consider for diabetes:
1. Basmati Rice: Basmati rice has a lower GI compared to many other rice types, making it a favorable choice for diabetics. It is also known for its distinct aroma and excellent flavor. Basmati rice provides carbohydrates with a lower impact on blood sugar.
2. Brown Rice: Brown rice is a whole grain that retains the bran and germ layers, making it higher in fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to white rice. Its fiber content slows down digestion, resulting in better blood sugar control.
3. Wild Rice: Wild rice is technically not rice but a type of grass seed. It has a lower GI than white rice and is rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Its earthy flavor and chewy texture can be a delightful addition to meals.
4. Red Rice: Red rice is another whole grain option that is higher in fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to white rice. It provides a nutty flavor and an appealing reddish hue to your dishes.
5. Black Rice: Also known as forbidden rice, black rice is packed with antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients. Its deep, dark color signifies its high nutritional value. Black rice can be a beneficial addition to a diabetes-friendly diet.
Conclusion
While these rice varieties are suitable for individuals with diabetes, it's crucial to practice portion control. Keep your serving sizes in check, and consider the overall composition of your meals. A well-balanced plate that includes lean proteins, non-starchy vegetables, and healthy fats alongside these rice varieties can help you achieve better blood sugar management.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
The Significance of Insulin Colour Coding in Diabetes Management
Insulin colour coding is an effective strategy in diabetes management, helping to identify different types of insulin and reduce the risk of medication errors. Standardised globally, these colours offer a simple yet valuable tool for enhancing patient safety. Combining this with lifestyle modifications, such as those offered by the Apollo Super 6 programme, can help manage diabetes more efficiently.
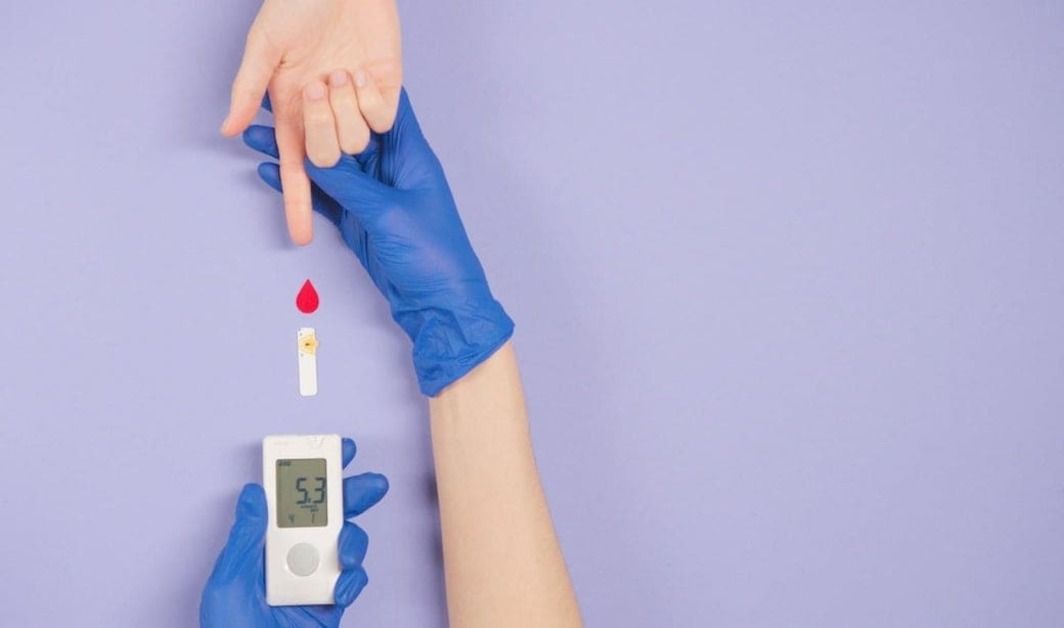
Diabetes Management
Why is it Important to Maintain Blood Sugar within Range?
A blood sugar level of 98 mg/dL falls within the normal range, signifying effective glucose regulation and metabolic stability. Regular monitoring and healthcare provider consultation offer a comprehensive understanding of metabolic health. While a consistent reading of 98 mg/dL is generally positive, individual health factors should be considered for accurate assessment.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help Lower Blood Sugar Levels?
Curious about the role of apple cider vinegar in managing blood sugar levels? While not a cure or replacement for medications, this common kitchen product may help manage your blood glucose levels when added to a comprehensive management plan. Remember, managing diabetes effectively also means making healthier lifestyle choices and having the right support. With programmes like Apollo Super 6, you can get the help you need to effectively manage your diabetes.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
The Significance of Insulin Colour Coding in Diabetes Management
Insulin colour coding is an effective strategy in diabetes management, helping to identify different types of insulin and reduce the risk of medication errors. Standardised globally, these colours offer a simple yet valuable tool for enhancing patient safety. Combining this with lifestyle modifications, such as those offered by the Apollo Super 6 programme, can help manage diabetes more efficiently.

Diabetes Management
Why is it Important to Maintain Blood Sugar within Range?
A blood sugar level of 98 mg/dL falls within the normal range, signifying effective glucose regulation and metabolic stability. Regular monitoring and healthcare provider consultation offer a comprehensive understanding of metabolic health. While a consistent reading of 98 mg/dL is generally positive, individual health factors should be considered for accurate assessment.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help Lower Blood Sugar Levels?
Curious about the role of apple cider vinegar in managing blood sugar levels? While not a cure or replacement for medications, this common kitchen product may help manage your blood glucose levels when added to a comprehensive management plan. Remember, managing diabetes effectively also means making healthier lifestyle choices and having the right support. With programmes like Apollo Super 6, you can get the help you need to effectively manage your diabetes.
