General Health
HbA1c Normal Range & Tips to Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
6 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 19 February 2025
Share this article
0
0 like
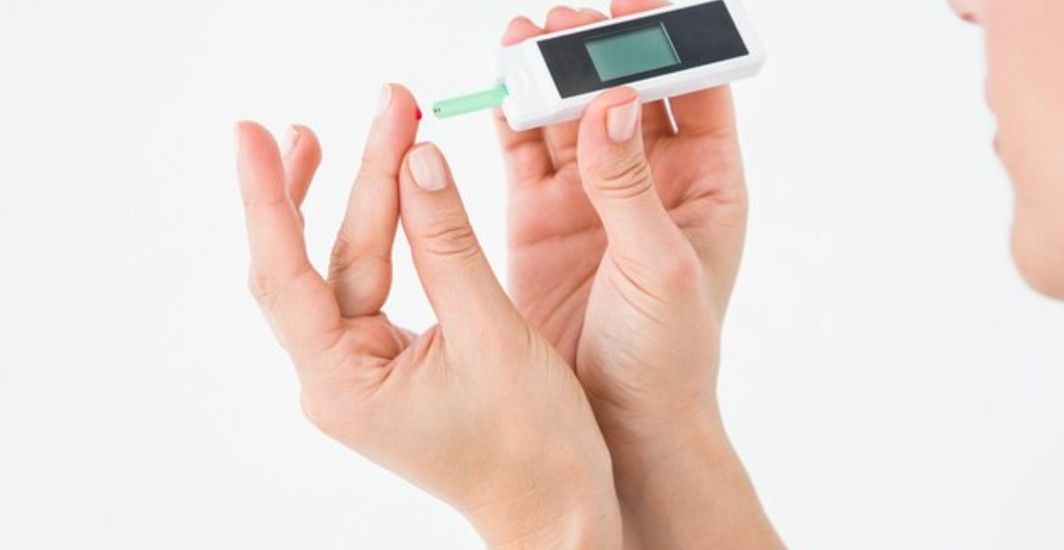
HbA1c, or glycated haemoglobin, is a key measure of your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. This compound forms when glucose in the blood binds to haemoglobin in red blood cells. Elevated HbA1c levels can increase the risk of diabetes-related complications, including issues with the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Regular testing is important, as even slight increases can lead to health concerns.
By understanding your HbA1c results, you can better manage your blood sugar. Implementing lifestyle changes, such as improving your diet and increasing physical activity, can help lower your levels and minimise the risk of complications. If your results are higher than normal, seeking tailored advice from a healthcare professional is essential.
What is an HbA1c Test?
The haemoglobin A1c test, also known as the HbA1c Test or the glycated haemoglobin test, assesses your average blood sugar levels. This test functions similarly to a baseball player’s batting average for a season—one game doesn’t reflect the player's overall performance, just as a single day’s results don’t provide a full understanding of your treatment's effectiveness.
A1c test results are vital for your doctor to determine if you have diabetes. They are also used to diagnose prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are elevated but not yet high enough to be classified as diabetes. If your A1c results indicate diabetes or prediabetes without symptoms, your doctor may suggest retesting on another day to confirm the diagnosis. For individuals with diabetes, regular A1c testing is crucial for tracking blood sugar control and assessing whether changes to medication are necessary.
Why is the HbA1c Test Important?
The HbA1c test is important because it provides an overall assessment of average blood glucose levels over a longer period. Unlike individual blood glucose readings, which can be affected by short-term factors such as stress, meals, or illness, the HbA1c test gives a more reliable measure of glycaemic control.
In addition, HbA1c results are essential for guiding treatment decisions for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes patients. They assist healthcare professionals in evaluating the effectiveness of current medications, lifestyle changes, and management strategies, indicating whether adjustments are needed. However, the importance of the HbA1c test goes beyond treatment management.
It also plays a key role in diagnosing diabetes and identifying individuals with prediabetes. Early detection through HbA1c testing facilitates timely interventions to prevent the progression to diabetes.
How do we Track HbA1c?
The HbA1c test can be performed in two ways:
1. Blood Draw from a Vein:
A phlebotomist will find a suitable vein, usually in the inner arm, clean the area, and insert a needle to draw blood into a test tube. The sample is then sent to a lab for analysis.
2. Blood Draw from a Finger Prick:
You select a finger, which the healthcare provider will clean. A lancet is used to prick the finger, and a drop of blood is collected in a test container for analysis.
Both methods provide the sample needed to determine your HbA1c levels.
When Should One Take an HbA1c Test?
The recommended timing for HbA1c testing is as follows:
- Individuals with Prediabetes: Testing is suggested annually.
- For Those Actively Managing Blood Sugar Levels: HbA1c should be checked every three months.
- Once Goals Are Met: If glycaemic control remains stable, patients with diabetes can transition to testing every six months.
The frequency of testing will depend on an individual's diabetes status, treatment approach, and level of control. It's important to consult a healthcare professional before having any tests.
You might need an A1c test if you have symptoms of diabetes, which can include:
- Intense thirst
- Increased urination
- Blurred vision
- Unexpected weight loss
- Ongoing fatigue
- Dry skin
What is the Normal HbA1c Level?
An HbA1c test assesses the percentage of haemoglobin bound to sugar, with the following categories defined by the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
- Normal (no diabetes): Below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: Between 5.7% and 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
The CDC recommends that individuals with diabetes aim for an HbA1c level of 7% or less. For those without diabetes, normal HbA1c levels typically range from 4% to 5.6%. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, which raises the risk of developing diabetes. A diabetes diagnosis is confirmed when levels reach 6.5% or more.
What’s a Dangerous Level of A1c?
An HbA1c level exceeding 9% significantly increases the risk of serious diabetes-related complications, such as:
- Vision impairment or blindness
- Kidney failure
- Diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage), which often impacts the hands, feet, arms, and legs
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Gastroparesis (stomach paralysis), which affects the stomach's ability to digest food properly
- It’s vital to maintain HbA1c levels below this threshold to reduce these health risks.
How to Lower HbA1c Levels?
Reducing HbA1c levels can help slow the progression of diabetes and lower the risk of complications, such as nerve damage and cardiovascular issues, for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Here’s a structured approach to consider:
1. Lifestyle Tips
- Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week, including 75 minutes of strength training. If you use insulin or have specific health concerns, consult your healthcare professional for a personalised exercise plan.
- Reduce Sitting Time: Avoid prolonged sitting by standing up and moving around every 30 minutes to help manage blood glucose levels.
- Engage in Routine Activities: Incorporate movement into everyday tasks like housework and gardening.
- Monitor Blood Glucose: Regularly check your blood glucose to track your progress and make adjustments as needed.
- Follow Your Treatment Plan: Stick to the medications and lifestyle changes recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Weight Management: If applicable, collaborate with a healthcare professional to establish realistic weight maintenance goals.
- Track Progress: Keep a record of your activities and blood glucose levels to help motivate you and identify effective strategies.
- Involve Others: Seek support from friends or family to encourage your lifestyle changes and maintain motivation.
2. Nutrition Tips
Be Mindful of Portion Sizes: Pay attention to how much you eat to avoid overeating.
- Avoid Skipping Meals: Regular meals can help keep blood sugar levels stable.
- Plan Meals Ahead: Preparing meals in advance can help you make healthier choices.
- Keep a Food, Medication, and Exercise Journal: Documenting these factors can help you recognise patterns and make necessary adjustments.
- Spread out Carbohydrate Intake: Distribute carbohydrate-rich foods throughout the day for better blood sugar control.
- Choose Whole, Less-Processed Foods: Opt for whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include a variety of healthy proteins, fats, and carbohydrates to ensure proper nutrition.
3. Key Dietary Trends for People with Diabetes
Include fruits and vegetables abundantly in your diet.
- Incorporate lean protein sources.
- Choose foods with little added sugar.
- Focus on healthy fats and limit trans fats.
- Reduce consumption of processed foods.
By following this structured approach, you can help maintain blood sugar and HbA1c levels within a healthy range.
Conclusion
HbA1c levels reflect the average blood glucose over the previous three months, and healthcare professionals utilise this measure for monitoring and diagnosing diabetes. A level of 6.5% or higher indicates that an individual may have diabetes.
Keeping HbA1c levels within a healthy range is crucial for minimising the risk of complications related to diabetes. Effective methods for managing blood sugar and HbA1c include following a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and adhering to a diabetes treatment plan. By incorporating these approaches, individuals can achieve better blood sugar control and improve their overall well-being.
General Health
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
General Health
ECG Test – Purpose, Procedure, Normal Range, and Results Interpretation
Understand the ECG Test: Learn about its purpose in checking your heart's electrical activity, the simple procedure, normal findings, and how doctors interpret the results to diagnose heart conditions.
General Health
The Role of MRI Scans in Detecting and Diagnosing Cancer
Discover the pivotal role of MRI scans in early cancer detection and diagnosis, offering insights for improved patient care.
General Health
These Exercises Can Reverse Muscle Ageing!
Everyone knows that doing exercise is good for us. Its numerous health benefits are widely known. It’s also not news that exercising helps in strengthening muscles and improving their health. However, did you know that it can also help in reversing muscle ageing altogether? There have been multiple studies conducted that prove this miraculous effect of physical activity.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Could There Be More to Your Snore?
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

General Health
ECG Test – Purpose, Procedure, Normal Range, and Results Interpretation
Understand the ECG Test: Learn about its purpose in checking your heart's electrical activity, the simple procedure, normal findings, and how doctors interpret the results to diagnose heart conditions.

General Health
The Role of MRI Scans in Detecting and Diagnosing Cancer
Discover the pivotal role of MRI scans in early cancer detection and diagnosis, offering insights for improved patient care.

General Health
These Exercises Can Reverse Muscle Ageing!
Everyone knows that doing exercise is good for us. Its numerous health benefits are widely known. It’s also not news that exercising helps in strengthening muscles and improving their health. However, did you know that it can also help in reversing muscle ageing altogether? There have been multiple studies conducted that prove this miraculous effect of physical activity.