General Health
APLA Test: How This Simple Blood Test Can Diagnose Serious Conditions
6 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 19 February 2025
Share this article
0
0 like
%20(2).jpg?tr=q-80)
APLA test is referred to as the Anti-Phospholipid Antibody test. This blood test is crucial for detecting abnormal immune system activity that can lead to severe conditions such as blood clotting disorders, recurrent pregnancy loss, and autoimmune diseases. If you've been experiencing unexplained symptoms or have a family history of certain medical conditions, this test could help identify potential risks early on.
In this article, we'll break down everything you need to know about the APLA test, including what it is, why it is necessary, who should consider getting it, how it's performed, and what the results might mean for your health.
What is the APLA Test?
The APLA test is a diagnostic blood test used to detect the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) in your bloodstream. Phospholipids are a type of fat molecule found in the membranes of your cells, and they play a vital role in normal blood clotting. However, in some cases, the body’s immune system mistakenly produces antibodies that target these phospholipids. This can lead to abnormal blood clotting and increase the risk of severe health conditions.
The APLA test is particularly valuable in diagnosing Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome (APS), a condition in which the body produces these antibodies and is more prone to abnormal clotting, leading to deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, stroke, and heart attack. Additionally, it is often used to help understand the cause of recurrent miscarriages in women who are otherwise healthy.
Why is the APLA Test Important?
The APLA test is essential for diagnosing various health conditions that may not have obvious symptoms in their early stages. By identifying antiphospholipid antibodies in the blood, doctors can gain insights into why certain individuals are at a higher risk for serious health complications like:
- Blood Clotting Disorders: People with high levels of antiphospholipid antibodies are more prone to forming blood clots in veins and arteries. These clots can lead to life-threatening conditions like pulmonary embolism or stroke.
- Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: APS has been linked to miscarriages, particularly in the first trimester. The presence of aPL antibodies can cause blood clots to form in the placental blood vessels, preventing a healthy pregnancy from progressing.
- Heart Disease: Anti-phospholipid antibodies may increase the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular issues due to abnormal clot formation.
- Neurological Disorders: The presence of these antibodies can also contribute to neurological conditions, including stroke or seizures.
- Other Autoimmune Diseases: APS is considered an autoimmune disorder and is often associated with conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. If you have one of these conditions, your doctor may recommend an APLA test to rule out or confirm the presence of APS.
Who Should Consider Getting the APLA Test?
The APLA test is typically recommended for people who are experiencing unexplained symptoms, have a family history of certain conditions, or have already been diagnosed with autoimmune diseases. Specific groups of individuals who may benefit from the test include:
- Individuals with Unexplained Blood Clots: If you've had multiple blood clots, especially at a young age, the APLA test can help determine whether anti-phospholipid antibodies are contributing to this issue.
- Women with Recurrent Miscarriages: If you've had two or more consecutive miscarriages, particularly in the early stages of pregnancy, your doctor may suggest this test to rule out APS as the underlying cause.
- People with Autoimmune Disorders: If you already have autoimmune conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, an APLA test may be advised to assess your risk for APS.
- People with Stroke or Neurological Issues: If you've had a stroke or experienced unexplained neurological symptoms, such as seizures, the APLA test may help uncover a potential cause related to blood clotting.
- People with a Family History of APS: If someone in your family has been diagnosed with APS, you may be at an increased risk of developing the condition yourself. Early testing can help detect any issues before they lead to complications.
How is the APLA Test Performed?
The APLA test is a relatively simple procedure. It requires a blood sample from your vein, usually taken from your arm. The test is typically performed in a laboratory, where your blood will be analysed for the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies.
The procedure involves the following steps:
- A healthcare professional will clean the area where the needle will be inserted.
- A needle will be used to draw a small amount of blood from your arm.
- The blood sample will be sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- It is a non-invasive and quick procedure with little to no discomfort. After the test, you may resume your normal activities right away.
What Does the APLA Test Results Mean?
The results of an APLA test are usually available within a few days, depending on the laboratory. The results are typically reported in terms of positive or negative:
- Positive Results: A positive result indicates that you have a higher level of anti-phospholipid antibodies in your blood. This suggests that you may have Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome (APS), which increases the risk of blood clotting, pregnancy complications, and other serious health conditions. However, a positive result does not automatically mean you will develop these complications. Additional tests and medical evaluations may be needed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
- Negative Results: A negative result means that there are no detectable anti-phospholipid antibodies in your blood, indicating a lower risk for blood clotting disorders and related complications. However, it is important to note that negative results do not completely rule out the possibility of APS, as antibody levels can fluctuate over time. In some cases, your doctor may recommend retesting after a period of time, especially if you continue to experience symptoms.
Treatment Options Following APLA Test Results
If your test results indicate the presence of anti-phospholipid antibodies, your healthcare provider will likely recommend a treatment plan tailored to your individual needs. Treatment for APS typically involves managing the symptoms and minimising the risks associated with blood clots. Common treatment options include:
- Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners): Medications like warfarin or heparin may be prescribed to reduce the risk of blood clot formation. These drugs help prevent clots from forming in the blood vessels.
- Aspirin: Low-dose aspirin therapy may be recommended to reduce the likelihood of clot formation, especially for people who are at risk for stroke or heart attack.
- Pregnancy Monitoring: For women with APS who are pregnant, regular monitoring and medical supervision are essential. In some cases, medications like heparin or aspirin may be used to prevent miscarriage and promote a healthy pregnancy.
- Addressing Underlying Conditions: If you have an autoimmune disease like lupus, treating the underlying condition can help reduce the risk of developing APS or other related complications.
Conclusion
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms or risk factors mentioned above, or if you're concerned about your health and want to take preventive measures, consider booking an APLA test. It’s a simple, non-invasive test that can provide valuable insights into your health and help detect potentially serious conditions early on. Early detection and appropriate treatment can significantly reduce your risk of complications and help improve your quality of life.
General Health
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
General Health
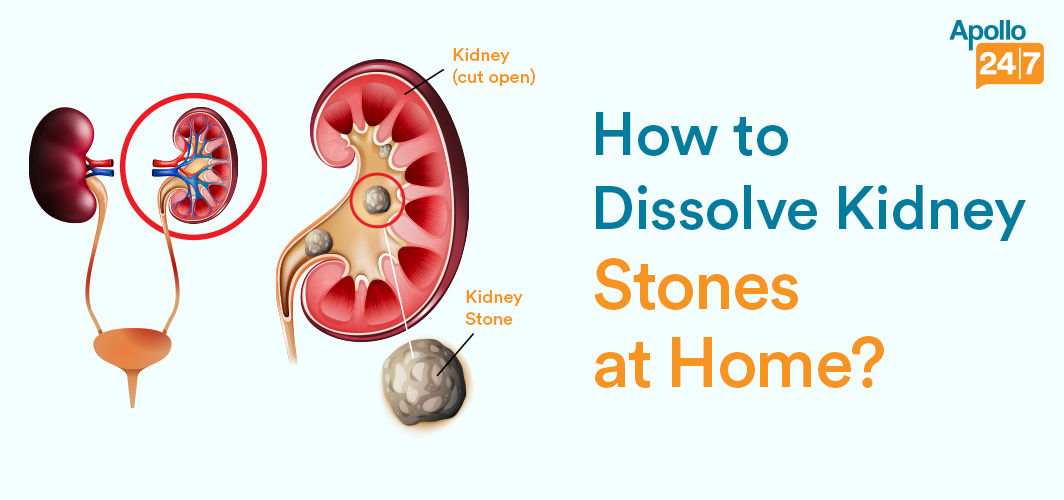
How to Dissolve Kidney Stones at Home?
Regardless of gender, any individual can develop kidney stones. Because of kidney stones, one can suffer from several symptoms that impact their daily lifestyle. In this blog, you can find home remedies that help you to dissolve kidney stones.

General Health
Night Owls Or Early Birds: Who’s More Likely To Develop Heart Ailments & Diabetes?
Researchers conducted a study that compared night owls, those who stay up late, with the early birds, those who are at their most energetic in the mornings. Read to know how these sleeping habits can affect people’s susceptibility to developing certain chronic diseases.
_14.jpg?tr=q-80)
General Health
I have a 7-month-old baby. Again I am pregnant for 2 months. I want an abortion. Please suggest me any medicine.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Science-backed Home Remedies for Burns and Blisters
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

General Health
How to Dissolve Kidney Stones at Home?
Regardless of gender, any individual can develop kidney stones. Because of kidney stones, one can suffer from several symptoms that impact their daily lifestyle. In this blog, you can find home remedies that help you to dissolve kidney stones.

General Health
Night Owls Or Early Birds: Who’s More Likely To Develop Heart Ailments & Diabetes?
Researchers conducted a study that compared night owls, those who stay up late, with the early birds, those who are at their most energetic in the mornings. Read to know how these sleeping habits can affect people’s susceptibility to developing certain chronic diseases.
_14.jpg?tr=q-80)
General Health