Diabetes Management
Adapting Your Diabetic Diet Plan to Suit Lifestyle and Preferences
1 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 28 February 2024, Updated on - 22 April 2024
Share this article
0
1 like
_1.jpg?tr=q-80)
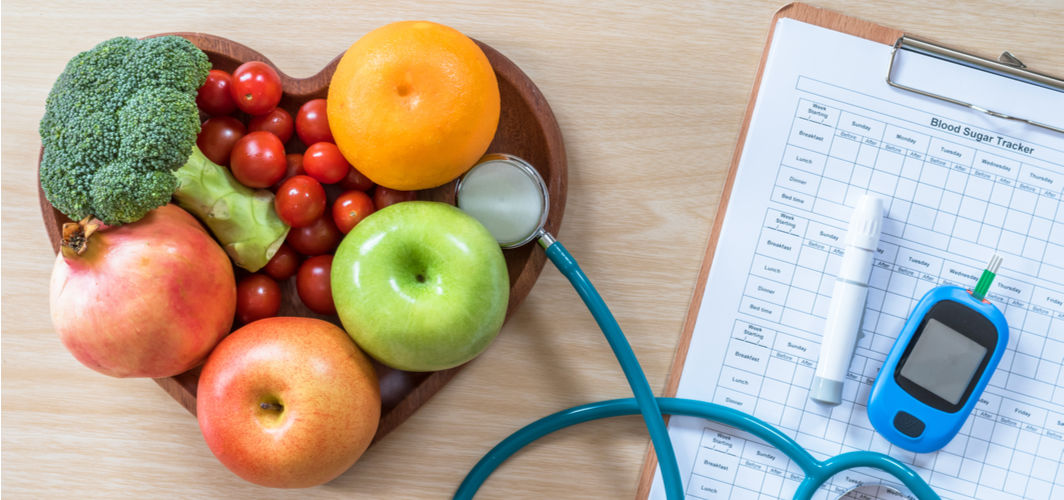
Studies reveal that a diet rich in trans fats, processed meats, and sugars increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Managing diabetes, thus, requires more than medication; it also demands a well-thought-out diet plan. Finding a diabetic diet plan that suits both, your personal lifestyle and individual food preferences is not as daunting as it may seem.
Understanding Carbohydrates and Proteins
Balancing carbohydrates and proteins is crucial for managing diabetes. Carbohydrates elevate blood sugar levels more directly than proteins, which help sustain glucose levels. It is suggested to opt for high-fiber carbs and lean protein for better control over diabetes.
- High-fiber carbohydrates: Foods like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are good sources.
- Lean protein: Include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, or plant-based proteins like lentils and chickpeas.
Monitor Portion Sizes
Controlling the amount you eat is as important as watching what you eat. Here are some pointers:
- Use smaller plates or bowls to naturally reduce portion size.
- Try to fill half your plate with vegetables both raw and cooked form for a nutrient-rich meal.
- Include 1 fruit every day in the mid-morning or breakfast for fiber and make up your daily intake of fruits.
Account for Physical Activity
Regular physical activity helps your body use insulin more efficiently. Remember to adjust your food intake or insulin doses on days with increased physical activity. It is advisable to consult your doctor before starting any new exercise regime.
The Benefit of Consultation
A registered dietitian can help you embark on an eating plan fitting your specific needs, considering factors such as glycemic control level, health issues, lifestyle factors, and personal preference.
In conclusion, finding the right balance in your diet can significantly aid your journey of managing diabetes.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
At What Stage of Pregnancy Can You Develop Gestational Diabetes?
Understanding when gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy can empower expecting mothers to take charge of their health. Typically developing during 24–28 weeks of pregnancy, it can occur earlier for those with certain risk factors. Regular monitoring and healthy lifestyle practices are key for effectively managing this condition.

Diabetes Management
Explained: The Diabetes and Heart Disease Link
Yes, diabetes can increase the risk of heart disease by affecting the blood vessels and promoting the buildup of plaque. Elevated blood sugar levels can damage the lining of blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis. Additionally, diabetes is associated with other risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol levels, further contributing to heart disease risk.
Diabetes Management
Can Diabetes Pass On To Generations?
Not only family history, there are other factors that can increase the risk of diabetes. These factors include being 45 years or older, a sedentary lifestyle, being obese or overweight, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, gestational diabetes, PCOS, stress and depression, and a history of heart disease. Individuals with two or more risk factors have a higher likelihood of developing diabetes compared to others.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
At What Stage of Pregnancy Can You Develop Gestational Diabetes?
Understanding when gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy can empower expecting mothers to take charge of their health. Typically developing during 24–28 weeks of pregnancy, it can occur earlier for those with certain risk factors. Regular monitoring and healthy lifestyle practices are key for effectively managing this condition.

Diabetes Management
Explained: The Diabetes and Heart Disease Link
Yes, diabetes can increase the risk of heart disease by affecting the blood vessels and promoting the buildup of plaque. Elevated blood sugar levels can damage the lining of blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis. Additionally, diabetes is associated with other risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol levels, further contributing to heart disease risk.

Diabetes Management
Can Diabetes Pass On To Generations?
Not only family history, there are other factors that can increase the risk of diabetes. These factors include being 45 years or older, a sedentary lifestyle, being obese or overweight, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, gestational diabetes, PCOS, stress and depression, and a history of heart disease. Individuals with two or more risk factors have a higher likelihood of developing diabetes compared to others.

